The Constitution Of India Pdf
PDF generated: 16 May 2018, 18:23 This complete constitution has been generated from excerpts of texts from the repository of the Comparative Constitutions Project, and distributed on constituteproject.org. Constituteproject.org India's Constitution of 1949 with Amendments through 2014. Mar 8, 2018 - Indian polity notes PDF download. Important articles of constitution of India. Committee, fundamental rights and duties.SubCommittees that.
Easy and Hand written Important Frequently Asked questions on constitution of India Download Constitution of India free PDF Question bank For General Knowledge for SSC/ UPSC Exams The Constitution of India is one of the important topics of Indian polity and the Constitution of India section is major topic to be studied for any of the Competitive Exams. The competitive exams like SSC, UPSC, IAS, FCAT, Railway Exams, CDS, State Civil Services exams have major questioning done from this section of polity. The candidates preparing for the civil service exam and other exams as mentioned need to learn polity section necessarily as many questions are being asked from this section. The candidates often get confused in this section that which features and sources of Constitution of India are to be studied. The candidates who are preparing for the SSC / UPSC exams need to have General Knowledge of the Indian Polity and Constitution of India. The easy way to learn the constitution of India is through the main topics to be studied.
We are providing the hand written questions to the candidates so that it becomes easy for the candidates to learn the constitution of India. We have summarised the important and frequently asked questions for the candidates and candidates are suggested to go through these questions and learn them and candidates will be able to score high in the examination. Also go through. Constitution of India Free PDF We are providing the candidates with handy, short and easy notes of Borrowed Features of constitution of India. The candidates who want to learn polity notes quickly should refer to this content. The major questions being asked in the exams are about the borrowed features that from which constitution which rule was taken or borrowed.
So candidates majorly need to learn these features for exams. The candidates preparing for exams like SSC, UPSC, IAS, FCAT, Railway Exams, CDS, State Civil Services will find it of great help, we have tried to make things easier for the candidates preparing for the competitive exams. Hope this may help you all. Please refer below content for the notes.
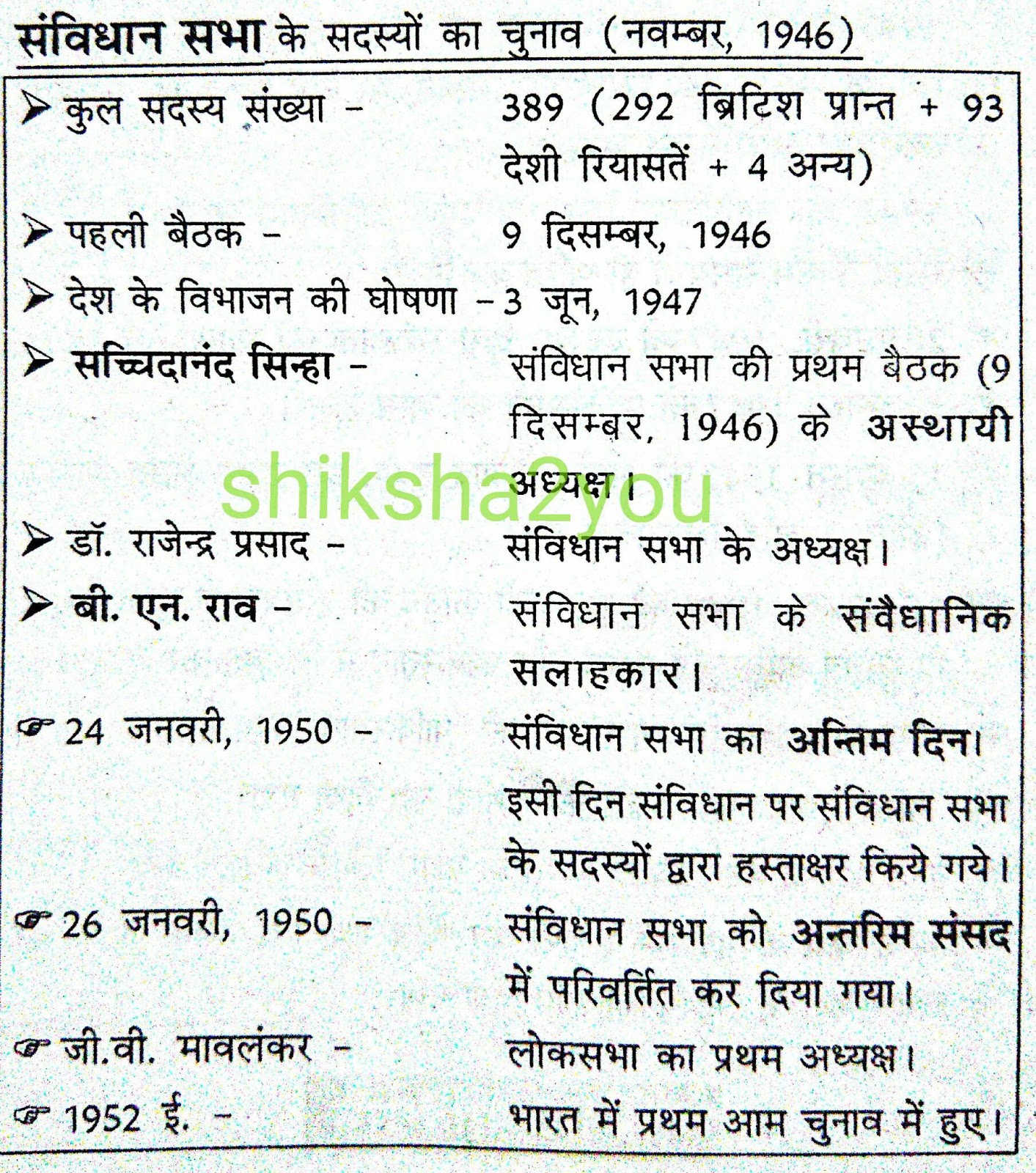
List of All 22 Parts of The Indian Constitution PDF are very important for all types of competitive examinations like Banking, railways, CGL, SSC, MTS, UPSC, IAS etc. So you have to remember all these parts for general knowledge. At present ( 2017 2018): Number of Parts 25 Total number of Articles 448 Total 12 Total Appendices 5 Number of Amendments 101 is the fundamental law of a country which ordains the fundamental principles on which the government of that country is based.
It lay down the framework and principle functions of various organs of the government as well as the modalities of interaction between the government and its citizens. Here is a brief description of all the 22 parts of the constitution of India. Part I: Article 1 to 4 belongs to part I of the Indian Constitution. This part deals with territory of India, formation of new states, alterations of areal boundary, names of existing states.
Part II: Part II contains Article 5 to 11. It deals with various rights of citizenship. Part III: Article 12 to 35. Deals with fundamental rights of Indian citizens. Article 31 dealing with the right to property was deleted by 44th amendment. Part IV: Article 35 to 51. Deals with Directive Principles of State Policy.
This policy aim at establishing social and economic democracy in the country. Part IV-A: Article 51-A. This part added by 42nd amendment in 1976. It contains the duties of the citizens. It out line the duties of the Indian citizens. Part V: Article 52 to 151. This part deals with government at the Union Level.
Duties and function of PM, Ministers, President Attorney General, Parliament – Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha, Comptroller and Auditor General. Article 77 stipulates that all executive orders of the Government of India shall be taken in the name of the President. Read More: Part VI: Article 152 to 237. Deals with government at State Level. Article 152 exempts Jammu and Kashmir form the category of ordinary States.
Duties and functions of Chief Minister and his ministers, Governor, State legislature, High Court, Advocate General of the State. Part VII: Article 238.
Deals with State, was deleted in 1956 by the 7th Amendment Act, 1956. Part VIII: Article 239 to 241. This part deals with Union Territories. Contains provisions regarding the administration of union territories. Part IX: Part IX consists of two parts. Added by 73rd amendment Act, 1992.
Contains a new schedule ‘Schedule Eleven”. It contains 29 subjects related to panchayat Raj.

They have been given administrative powers. Added by 74th amendment Act, 1992. It contains a new schedule “Schedule Twelve”. It contains 18 subjects related to Municipalities. They have been given administrative powers. Part X: Article 244 and 244-A belongs to this part. It deals with Scheduled and Tribal Area.
You may like: part XI: Article 245 to 263 belongs to this part. It deals with relation between Union and States and deals with legislative relations. Part XII: Article 264 to 300. Deals with distribution of revenue between Union and States, appointed of Finance Commission contracts, liabilities etc. Part XIII: This part contains Article 301 to 307. It relates to trade, commerce and intercourse within the Territory of India. Part XIV: Article 308 to 323.
It deals with UPSC and Public Service Commissions. Part XIV-A: Article 323a, and 323B are contained in this part.
Article 300a Of The Constitution Of India Pdf
It added by 42nd amendment in 1976. Deals with administrative tribunals set up by Parliament to hear disputes and complaints regarding Union, States or local govt. Also Read: Part XV: Article 324 and 329 are belong to this part.
It deals with elections or election commission. Part XVI: Article 330 to 342. Deals with special provisions for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes and Anglo-Indian Representation.
Part XVII: This part contains Article 343 to 351. It relates to the official language. Part XVIII: Article 352 to 360. It deals with emergency provisions.
Part XIX: Article 361 to 367. Exemption of criminal proceedings for their official acts of President and Governors.
Part XX: Only Article 368 contain in this part. It deals with amendment of the constitution. Part XXI: Article 369 to 392. Article 369 gives temporary powers to the Parliament to make laws for State list. Article 370 contains temporary provisions of Jammu and Kashmir. It restricts the parliament to make laws for that state.
Article 371-A to 371-I relates to special provisions for Maharashtra, Nagaland, Manipur, Sikkim, Mizoram, and Goa. Part XXII: This part contains Article 393 to 395. It concerns the short title, commencement and repeal of the Constitution. Although the systems of ancient India do have their reflections in the Constitution of India, the direct sources of the Constitution lie in the administrative and legislative developments of the British period.
Download 22 Parts of The Constitution of India PDF.
